Molly, or MDMA, has become synonymous with the electric energy of music festivals and late-night raves. If you’ve ever been curious about how long that euphoric high actually lasts, the answer is more nuanced than you might think.
Understanding the timeline means distinguishing between the duration of the high itself and how long the substance lingers in your body afterward.
Throughout this article, I’ll walk you through what to expect during a typical MDMA experience, the factors that can extend or shorten its effects, what the comedown feels like, and how long it remains detectable in various drug tests.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice—always consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
How Does MDMA Work in the Body?
MDMA works by flooding your brain with serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine: neurotransmitters responsible for mood, pleasure, and energy.
This massive release creates the signature effects: intense euphoria, heightened empathy, and a surge of physical energy.
Once you take MDMA, your liver enzymes begin breaking it down through metabolism. The half-life of MDMA sits around eight to nine hours, meaning that’s how long it takes for half the dose to leave your system.
This metabolic process directly influences how long you feel the effects and how quickly your body clears the substance entirely.
Timeline of Molly’s Effects: How Long Does Molly Last

MDMA doesn’t hit instantly; it unfolds in distinct phases that shape your entire experience. Here’s how the timeline typically progresses from the first sensations to the aftermath.
1. Onset Phase
The initial wave begins subtly, with a gradual build of energy and alertness. You might notice a tingling sensation, increased heart rate, or a sudden shift in mood as the drug enters your bloodstream.
Emotional warmth starts to emerge, and physical sensations become more pronounced. This is your body’s first response as MDMA begins releasing neurotransmitters, setting the stage for the more intense effects ahead.
How Long It Lasts: 20–60 minutes after ingestion.
Organ Sensitivity: The liver begins metabolizing MDMA immediately, while the heart rate and blood pressure start to elevate.
2. Peak Phase
This is where MDMA delivers its most powerful effects. Euphoria becomes overwhelming, colors appear more vivid, and music feels deeply immersive.
Emotional barriers dissolve, creating intense feelings of connection and empathy toward others. Physical touch becomes pleasurable, and many experience jaw clenching or teeth grinding.
The peak represents the highest concentration of MDMA in your system, when serotonin flooding reaches its maximum impact on your brain.
How Long It Lasts: 2–4 hours typically.
Organ Sensitivity: The brain experiences maximum serotonin depletion, while the cardiovascular system remains under significant strain.
3. Comedown & After-Effects
As MDMA leaves your system, the crash begins. Fatigue sets in heavily as your brain struggles with depleted serotonin levels.
Low mood, irritability, and difficulty concentrating become common complaints. Sleep patterns get disrupted even though exhaustion is overwhelming.
Some people experience anxiety or depression during this phase. Your body is essentially recovering from the neurochemical imbalance, working to restore normal function after the intense high.
How Long It Lasts: 1–2 days after use.
Organ Sensitivity: The brain works to replenish serotonin stores, while the body recovers from dehydration and physical exertion.
Factors That Influence How Long Molly Lasts
The duration of MDMA’s effects isn’t identical for everyone. Several variables can extend or shorten your experience, from what you take to how your body processes it.
- Dose Size and Purity: Higher doses prolong effects, while adulterants or cutting agents can create unpredictable timelines and intensities.
- Method of Consumption: Swallowing a pill takes longer to kick in than snorting powder, which hits faster but may wear off more quickly.
- Individual Metabolism: Your weight, genetic makeup, and liver function determine how rapidly your body breaks down MDMA.
- Mixing With Other Substances: Combining MDMA with alcohol, stimulants, or SSRIs can dangerously alter effects and duration.
- Physical Environment: Dancing intensely for hours increases body temperature and dehydration, potentially intensifying and extending the experience.
These factors interact in complex ways, making each person’s experience with MDMA uniquely timed and potentially unpredictable.
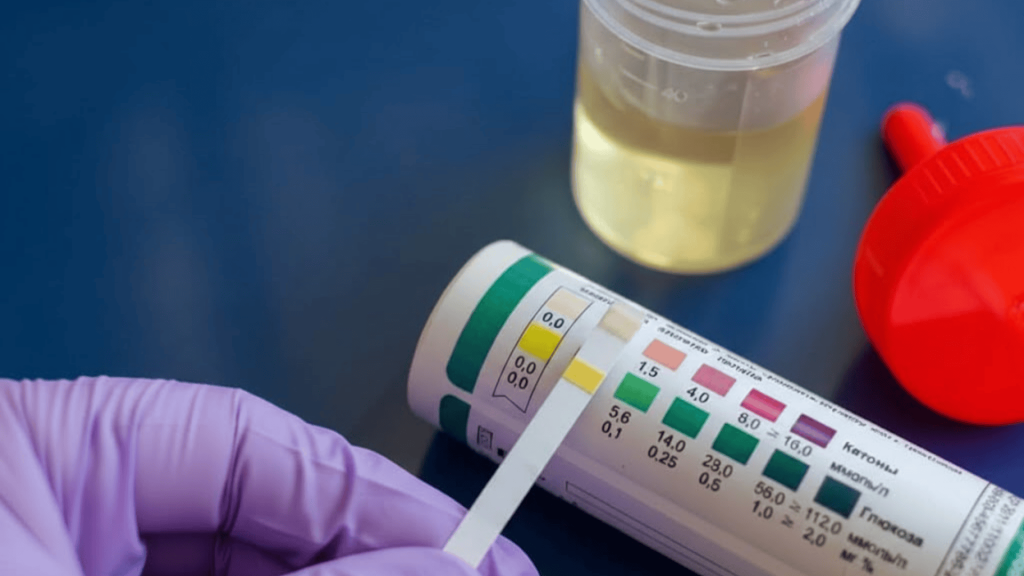
How Long Does Molly Stay in Your System?
Even after the high fades, MDMA remains detectable in your body for varying lengths of time depending on the type of test used. Detection windows differ significantly across biological samples.
| Test Type | Detection Window | Common Use Cases | Factors That Extend Detection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urine | 1–3 days (up to 4) | Employment screening, probation monitoring | Higher doses, chronic use, and slower metabolism |
| Blood | ~12–24 hours | Hospital emergencies, DUI investigations | Recent high-dose consumption, impaired liver function |
| Saliva | 1–2 days | Roadside testing, workplace spot checks | Oral dosing method, dehydration |
| Hair | Up to 90 days | Pre-employment, legal proceedings | Repeated use, darker/thicker hair retains more |
Risk Advisory: Detection times aren’t fixed; they shift based on dose size, frequency of use, and individual metabolism. Body weight, hydration status, and existing health conditions all influence how long MDMA lingers in your system.
Risks of Extended or Repeated Use

Using MDMA frequently or in high doses compounds the risks beyond a single experience. Your body and brain face mounting challenges when given little time to recover.
Immediate Physical Risks
MDMA significantly raises body temperature, especially in hot environments or during intense physical activity. Hyperthermia can become life-threatening without proper hydration and cooling breaks.
Dehydration worsens as the drug suppresses thirst signals while increasing sweating. Overdrinking water creates its own danger: hyponatremia, where sodium levels drop dangerously low.
These physical stressors strain your cardiovascular system and kidneys simultaneously.
Neurological and Psychological Consequences
Repeated MDMA use severely depletes serotonin reserves, leaving your brain chemically imbalanced. This manifests as persistent depression, heightened anxiety, and difficulty experiencing pleasure from everyday activities.
Sleep patterns become increasingly disrupted, creating a vicious cycle of exhaustion and mood instability.
Frequent use may cause long-term neurotoxicity, potentially damaging serotonin-producing neurons and impairing memory, cognition, and emotional regulation permanently.
Harm Reduction Tips if You Use MDMA Despite the Risks
If you decide to use MDMA despite the risks, certain precautions can reduce potential harm. These strategies won’t eliminate danger, but they may help minimize serious complications.
- Balance Hydration Carefully: Drink water steadily but moderately, roughly one small glass per hour, to avoid both dehydration and dangerous overhydration.
- Regulate Body Temperature: Take regular breaks from dancing, step outside for fresh air, and remove excess layers to prevent overheating.
- Test Your Substance: Use reagent testing kits to identify adulterants like PMA or synthetic cathinones, which can be far more dangerous than pure MDMA.
- Avoid Polydrug Use: Never combine MDMA with alcohol, other stimulants, or antidepressants, as interactions can be unpredictable and life-threatening.
- Plan Recovery Time: Allow at least several weeks between uses to let your brain replenish serotonin and reduce the risk of long-term damage.
No amount of preparation makes MDMA use completely safe, but informed decisions and cautious practices can significantly lower the odds of severe outcomes.
Resources & References: Evidence-Based Information on Molly
For evidence-based information on MDMA, the National Institute on Drug Abuse provides comprehensive research on effects and risks. The DEA’s fact sheet offers essential basics about the substance.
If you or someone you know struggles with substance use, the SAMHSA National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357 provides free, confidential support available 24/7.
The Drug Policy Alliance offers harm reduction resources grounded in public health approaches. These organizations provide reliable information to help you make informed decisions about MDMA use and recovery options.
The Bottom Line
Understanding how long Molly lasts goes beyond just tracking the hours of euphoria.
From that initial rush to the difficult comedown, plus how detection windows work across different tests, the timeline is more complex than most people realize.
The reality is that MDMA affects everyone differently based on dose, metabolism, and environment. If this information raised questions or you have personal experiences to share, drop a comment below.
Your insights could help someone else navigate these decisions more safely. Stay informed, stay cautious, and prioritize your well-being above everything else.