You’ve probably heard people talking about new cannabinoids like THCP and THCA. I’ve seen curiosity increasing fast. “Which one gets me high?” “Which one is legal?” “Which one is better for wellness?”
This post will help you cut through the buzz. I’ll show you what these compounds are, how they affect you, how they’re used, and what the safety and legal deal is.
By the end, you’ll be able to decide which might make sense for you, whether you’re chasing wellness without intoxication or more psychoactive effects.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not promote or encourage the use of THCP, THCA, or any cannabis-derived products. Laws and regulations vary by state and country, and information may change over time.
THCP vs. THCA: Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) | THCA (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid) |
|---|---|---|
| Discovered | 2019, found in trace amounts in cannabis. | Naturally present in raw cannabis; known since the 1960s. |
| Chemical Form | Psychoactive cannabinoid with a seven-carbon side chain. | Non-psychoactive acidic form of THC with a carboxyl group. |
| Psychoactivity | Strong. Binds to CB1 receptors ~30× more strongly than THC in lab tests. | None until heated (converts to THC through decarboxylation). |
| Relative Potency | Feels 5–10× stronger than THC in real-world use. | Converts into THC’s potency when heated. |
| Typical Effects | Strong euphoria, deep relaxation, longer high. | Clear-headed, calm, possibly anti-inflammatory, and wellness effects. |
| Duration | Long-lasting (up to 6+ hours). | Minimal in raw form; depends on conversion. |
| Common Uses | Potent relief, recreational use, sleep aid. | Wellness, inflammation, and daily support without intoxication. |
| Legal Status (U.S.) | Gray area: hemp-derived forms may be allowed but restricted in states. | Legal if hemp-derived (<0.3% Delta-9 THC), but heating can change legality. |
| Drug Test Risk | High. Shows positive for THC metabolites. | Can test positive if heated (converted to THC). |
Overview of THCP and THCA
THCP is short for tetrahydrocannabiphorol. Discovered in 2019, this compound was found in very small amounts in cannabis. It’s part of the same family of compounds derived from the precursor molecule called, roughly, CBG (cannabigerol).
THCA stands for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid. It’s the “raw” or acidic form of THC found naturally in the cannabis plant before any heating or processing. It too originates from the same basic plant chemistry as CBG.
In my experience, knowing that THCA is non-intoxicating in its raw form helps a lot of people feel more comfortable exploring it.
Both share a root with THC but differ in structure, behavior, and effect, and we’ll unpack those differences next.
Chemical and Structural Differences between THCA and THCP
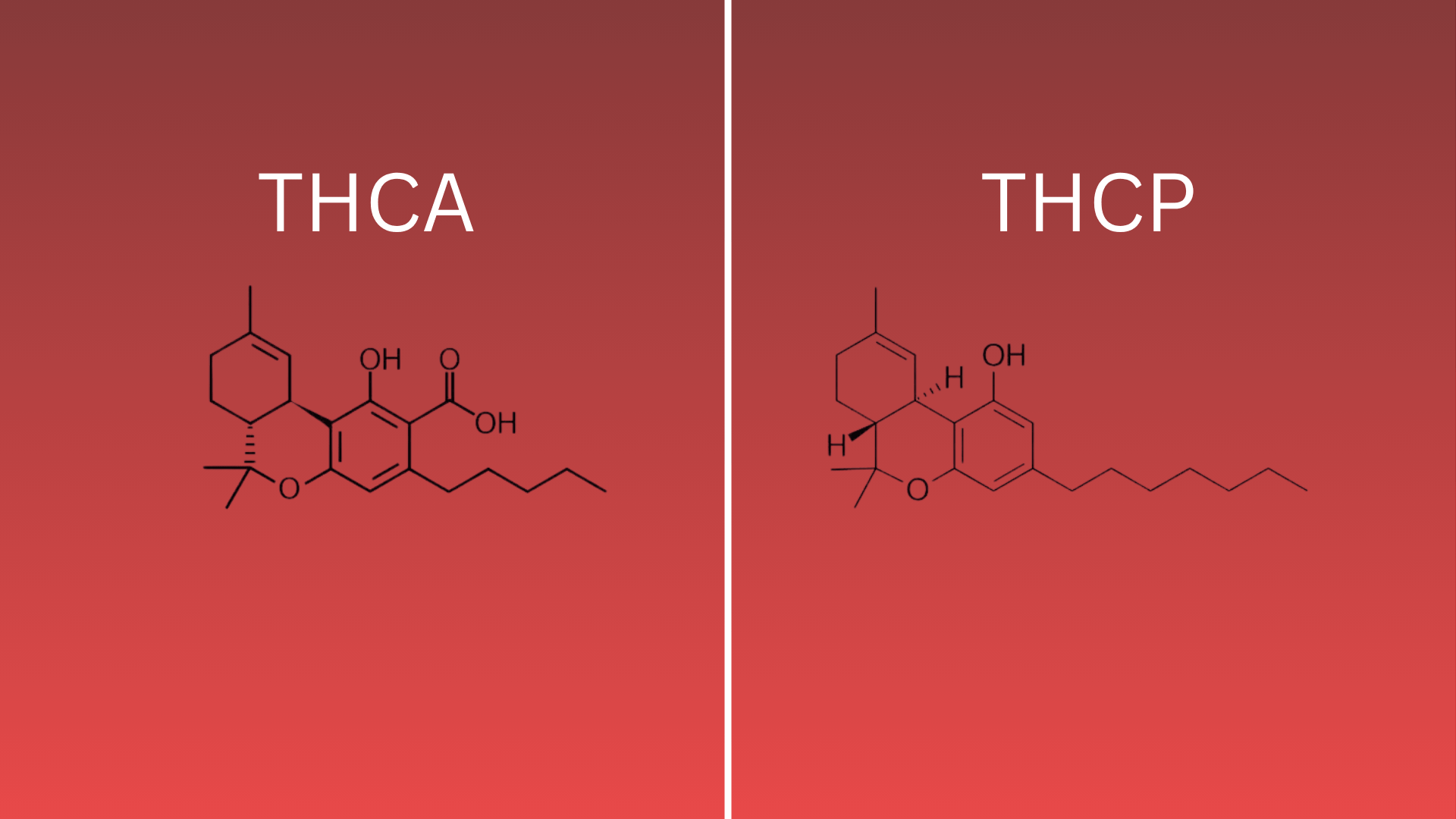
THCP has a longer side chain (seven carbon atoms) compared to THC’s usual five-carbon side chain. That extra length changes how strongly it binds to the body’s cannabinoid receptors.
THCA carries an acidic (carboxyl) group, making it the “acid” form. Because of that acid group, it’s mostly non-psychoactive until it’s heated, when it loses that acid group and becomes THC.
Think of THCP as a more power-packed version of what THC does. Think of THCA as the “pre-THC” version; it’s there, but locked until you apply heat or processing.
It helps to imagine a simple diagram showing two molecules side by side: THCP with its long chain, THCA with the acid tag. Visuals really help the concept stick.
Comparing Potency and Psychoactivity of THCA, THC, and THCP
Let’s compare how strong these compounds are and how they act.
| Compound | Psychoactivity | Relative Potency vs THC |
|---|---|---|
| THCA | None (raw) | Converts to THC when heated |
| THC | Typical high | Baseline (1×) |
| THCP | Strong, high | Up to ~33× binding affinity in lab tests |
THCP binds to CB1 receptors (the ones in the brain tied to “high” effects) up to about 33 times more strongly than standard THC in lab settings. That doesn’t always mean you’ll feel 33 times higher.
Real-world effects vary. But reports show THCP gives stronger and longer effects than many THC products when used.
THCA doesn’t make you high in its raw form. That’s because the acid group prevents strong interaction with the CB1 receptors.
When you apply heat (smoking, vaping, cooking), THCA undergoes decarboxylation, which removes the acid group and converts it into THC (which can then be psychoactive).
So, if you’re looking for a strong “high,” THCP may fit. If you want non-intoxicating, THCA in raw form is safer.
Effects of THCP and THCA
THCP and THCA act very differently in the body, especially when it comes to psychoactive effects and how strongly you feel them.
THCP Effects
In my experience and from what I’ve seen reported, THCP produces strong euphoria, altered perception, and a deeper body high. Because it binds more strongly to CB1 receptors, even smaller doses can feel intense.
However, that potency also means side effects can appear more easily, things like dizziness, anxiety, or nausea if you take too much. Overdoing it is simple with THCP, which is why “start low and go slow” really matters.
THCA Effects
THCA, in contrast, is non-intoxicating in its raw form. You won’t get a “high” unless it’s heated and converted to THC. Most people describe the experience as clear-headed and balanced, with little to no psychoactive shift.
If you’re seeking relaxation or focus without the typical THC “buzz,” THCA is the milder, more approachable option.
Benefits of THCP and THCA
Each cannabinoid offers unique potential benefits depending on your goals, body chemistry, and comfort with psychoactive effects.
THCP Benefits
- Pain relief: May help ease chronic or acute discomfort.
- Appetite stimulation: Often boosts hunger, supporting recovery or weight management.
- Relaxation and sleep: Can promote deeper rest and mental calm.
- Extended duration: Effects may last significantly longer than THC.
Because it’s highly potent, start with a very small dose. Overuse can easily lead to dizziness, anxiety, or nausea. THCP is best suited for experienced users seeking stronger physical or emotional relief.
THCA Benefits
- Anti-inflammatory properties: May help reduce swelling or joint discomfort.
- Neuroprotective effects: Early research shows possible brain and nerve support.
- Immune modulation: Could help stabilize the body’s natural defense system.
- Anti-nausea and appetite support: May ease queasiness and maintain appetite naturally.
Because it doesn’t produce a “high,” THCA fits well into daily wellness routines, especially for those focused on calm support, joint health, or clear-headed energy.
If your goal is gentle balance and steady well-being, THCA is the safer, more stable choice.
Consumption Methods of THCP and THCA

How you take each compound changes both the effect and the safety.
THCP is mostly found in vapes, gummies, distillates, and infused flower. Because of its potency, dosing matters a lot.
THCA is often used in raw flower, leafy form, juicing fresh cannabis plant material, or in capsules and oils that avoid heating.
Heating changes everything. If you apply heat to THCA, it converts into THC (psychoactive). If you vape or smoke THCP, you’re activating its full potency.
For non-intoxicating use of THCA, avoid heat. For psychoactive use of THCP, heat or another activation method is standard.
Legal Status & Drug Testing for THCP and THCA
Legal lines around cannabinoids get blurry fast; I’ll help you navigate them.
For THCP, it occupies a gray area. It’s derived from the cannabis plant and often from hemp-derived cannabinoids, so some U.S. hemp laws may apply. But because it behaves like a strong psychoactive cannabinoid, regulators are paying attention.
For THCA, in the U.S., hemp-derived THCA flower with less than 0.3% delta-9 THC by dry weight may be legal in some states under the 2018 Farm Bill. But because THCA can convert into THC when heated, legal risk remains in some jurisdictions.
Both THCP and THCA can lead to positive results for THC metabolites on a drug test (especially if you heat THCA and convert it into THC). So if you’re subject to testing, both carry risk.
State-by-state rules vary widely. Always check local law. Neither is totally safe nor legal everywhere. Caution and local knowledge matter.
Safety and Side Effects
Let’s talk about staying safe while exploring these compounds.
Short-term side effects include dizziness, anxiety, nausea, and increased heart rate. Especially with THCP, these may present more strongly.
Long-term research is very limited for both THCP and THCA; we don’t know many effects decades down the line.
Tips for responsible use:
- Start with a small dose, especially THCP.
- Choose lab-tested products from reputable brands.
- Avoid mixing with alcohol or other sedatives.
- If you feel uneasy, stop and rest.
- If you’re pregnant, have heart issues, or are on medication, consult a doctor before use.
THCP vs. THCA for Specific Needs
Here’s a simple guide to which one might suit your goals.
For pain relief: If you want strong relief and don’t mind psychoactive effects, THCP might be useful. But if you want relief without feeling “high,” THCA is a gentler pick.
For relaxation or euphoria: THCP is the clear winner if you’re looking to feel something more profound. THCA won’t deliver that kind of psychoactive shift.
For daily wellness: THCA tends to shine here; non-intoxicating, allowing you to stay clear-headed while exploring potential benefits.
For avoiding intoxication: THCA is your go-to. It lets you stay functional while possibly gaining therapeutic benefits. THCP requires more caution.
Think about your purpose, your tolerance, and your legal setting. If you’re new or cautious, THCA might be the safer starting point.
If you’ve used THC before, know your limits, and want something stronger, THCP could be considered, but with care.
Conclusion
In my view, both THCP and THCA have unique roles, and the best choice depends on what you’re looking for and your experience level.
THCA offers potential wellness benefits without intoxication, making it a great fit for daily or therapeutic use focused on balance, clarity, and long-term well-being.
THCP, on the other hand, delivers powerful effects but demands caution, patience, and responsible dosing, especially for those new to potent cannabinoids or high-THC products.
Remember, legality, dosing, and research for both are still developing. Make smart choices, verify lab results, check product quality, and when in doubt, consult a professional. Stay safe, informed, and mindful of your body’s response.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is THCP natural or synthetic?
THCP occurs naturally in very small amounts in cannabis plants, though many commercial products are synthesized for practical use.
Will THCA show up on a drug test?
Yes. If THCA is heated and converts into THC, it can lead to positive THC metabolite results.
Can I use both together?
Technically, yes, but combining them increases complexity and risk; it’s wise to know the dose and effects separately first.
Which is better for anxiety?
If you want to avoid intoxication, THCA may be better. If you seek a stronger effect, THCP might help, but it may also increase anxiety.
Is THCP safe for beginners?
As a beginner, proceed with extreme caution. THCP’s potency means small doses can have strong effects; start low and go slow.