I’ve been asked about codeine detection more times than I can count, and it’s a question that matters if you’re managing prescriptions, preparing for a drug test, or simply curious about how your body processes medications.
Here’s what I’ve learned: codeine doesn’t just disappear the moment you feel better. Detection windows shift depending on which test you’re taking and your unique body chemistry.
I’m going to walk you through exactly how long codeine lingers in your system, what shows up in urine versus blood versus saliva and hair tests, and why your metabolism plays such a crucial role in these timelines.
The information I’m sharing here is for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical, legal, or professional advice. Always consult with qualified healthcare providers or legal professionals regarding your specific situation, medication use, or any concerns about drug testing.
How Codeine Works in the Body?
Once you take codeine, your liver gets to work converting it into morphine through a process involving the enzyme CYP2D6.
This morphine is what actually provides pain relief by binding to opioid receptors in your brain and spinal cord, dulling pain signals, and suppressing cough reflexes.
Here’s the interesting part: how quickly your body performs this conversion directly impacts detection times. If you’re a fast metabolizer, codeine clears your system more rapidly. Slow metabolizers hold onto it longer.
Your liver then breaks down these compounds into metabolites that eventually leave through urine, which is exactly what drug tests look for.
Codeine Detection by Test Type
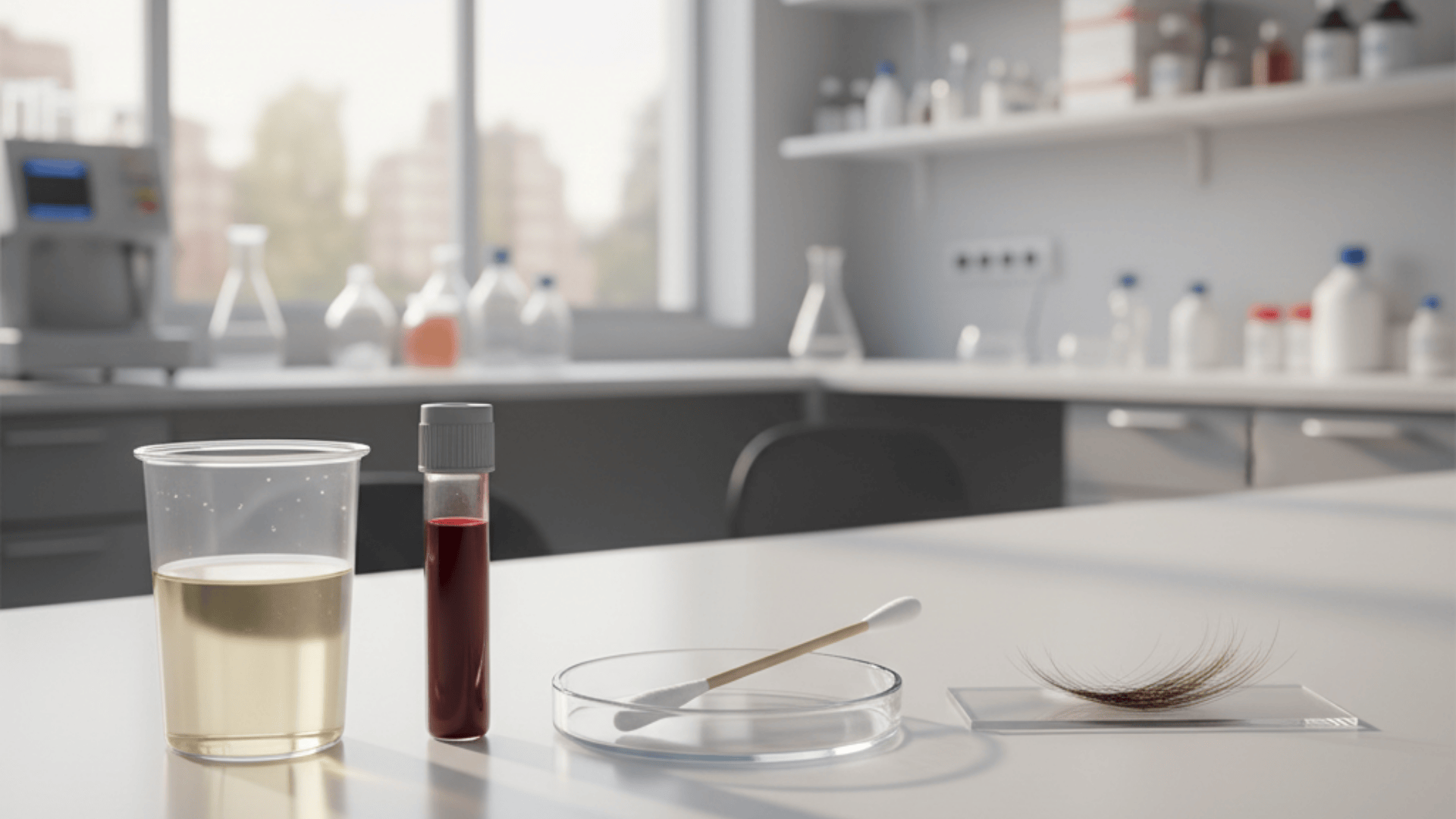

Different drug tests catch codeine at different stages of elimination. Understanding these detection windows helps you know what to expect depending on which screening method is used.
1. Urine Tests
Urine testing remains the gold standard for codeine detection in most workplaces and medical settings. I’ll tell you why it’s so popular: it’s affordable, non-invasive, and highly reliable.
For most people taking therapeutic doses, codeine and its metabolites show up in urine for one to two days after the last dose.
However, if you’ve been using codeine frequently or at higher doses, that window extends considerably, sometimes up to three or four days, because your body accumulates more of the drug and its breakdown products.
Testing Advantage: Urine tests offer an excellent balance between detection sensitivity and practical timeframe, making them ideal for routine screening.
2. Blood Tests
Blood testing provides the most accurate snapshot of active codeine in your system right now. Medical professionals and forensic investigators prefer this method when they need to know current impairment levels or recent use.
The catch is that codeine clears from the blood rapidly, typically within twelve to twenty-four hours after your last dose.
This makes blood tests useful for acute situations like emergency room visits or accident investigations, but less practical for detecting use that happened days ago.
Testing Advantage: Blood tests deliver real-time accuracy for determining active intoxication or very recent codeine use.
3. Saliva Tests
Saliva testing has gained popularity because it’s completely non-invasive and difficult to tamper with during collection. I find this method particularly interesting because it mirrors blood concentration levels fairly closely.
Codeine typically remains detectable in saliva for one to two days, though this can vary based on dosage and individual metabolism.
Law enforcement often uses saliva tests during roadside checks because results come back quickly and the collection process is straightforward and dignified.
Testing Advantage: Saliva tests provide quick, tamper-resistant results with minimal invasion and discomfort for the person being tested.
4. Hair Tests
Hair follicle testing stands apart from all other methods with its impressive detection window of up to ninety days or even longer.
Here’s how it works: as your hair grows, it incorporates drug metabolites from your bloodstream, creating a permanent record. This method can distinguish between one-time experimentation and chronic use patterns by analyzing different sections of the hair strand.
While hair tests are more expensive and take longer to process, they’re invaluable for situations requiring long-term use history.
Testing Advantage: Hair tests provide an extended historical record of codeine use that no other testing method can match.
Factors That Affect How Long Codeine Stays in Your System
Here’s something most people don’t realize: two individuals taking the same codeine dose can have completely different detection windows.
Your body’s unique characteristics determine whether codeine clears in hours or lingers for days. Let me show you exactly which factors tip the scales.
| Factor | Impact on Detection | Why It Matters | Typical Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage & Frequency | Higher and repeated doses extend detection | More codeine accumulates, creating more metabolites to clear | Can add 1–3 days to standard windows |
| Liver Function & Genetics | CYP2D6 enzyme activity determines speed | Liver converts codeine; genetics controls enzyme efficiency | Varies from 50% faster to 200% slower |
| Age & Body Composition | Older adults and higher fat percentages slow clearance | Reduced organ efficiency and fat storage prolong the elimination | May add 30–50% to detection time |
| Hydration Status | Dehydration slows metabolite excretion | Kidneys need fluids to filter and flush effectively | Poor hydration adds 12–24 hours |
| Drug Interactions | Certain medications alter metabolism | Antidepressants, antifungals inhibit processing enzymes | Can extend the window by 1–3 days |
| Kidney & Organ Health | Impairment delays elimination | Compromised organs can’t filter metabolites efficiently | Severe impairment may triple the clearance time |
These factors don’t operate independently; they combine and interact. Someone with excellent liver function but poor hydration might still show extended detection times.
How Long Do Opioids Stay in Your System?
Codeine isn’t alone in the opioid family, and each member has distinct detection characteristics.
Morphine, what codeine converts into, typically stays detectable in urine for two to three days, similar to codeine itself. Oxycodone, a stronger pain reliever, shows up for one to four days, depending on formulation. Hydrocodone mirrors this timeline at two to four days.
Here’s the pattern I’ve noticed: more potent opioids don’t necessarily stay longer, but they’re detectable at lower concentrations.
Fentanyl, despite its extreme potency, clears within one to three days in urine but can appear in hair tests for months, just like codeine.
Tips for Faster Codeine Clearance

I get asked constantly if there’s a way to speed up codeine elimination, and I always give the same honest answer: time is the only guaranteed solution.
That said, supporting your body’s natural detoxification systems can help optimize the process within safe limits.
- Stay Well-Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water supports kidney function and helps flush metabolites through urine more efficiently.
- Engage in Regular Exercise: Physical activity boosts circulation and metabolism, potentially aiding your body’s natural elimination processes.
- Eat a Balanced, Nutrient-Rich Diet: Supporting liver health with whole foods helps maintain optimal drug metabolism and detoxification pathways.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Rest allows your organs to function at peak efficiency during the elimination process.
- Avoid Additional Substances: Alcohol and other drugs strain your liver and kidneys, slowing down codeine clearance significantly.
Let me be clear about something important: no amount of water, exercise, or supplements will dramatically accelerate codeine elimination. Your body processes drugs at its own pace based on the factors we discussed earlier.
Risks of Testing Positive for Codeine
Testing positive for codeine can create serious complications in your life, even when you’re taking it legally with a prescription.
Understanding these potential consequences helps you navigate testing situations with confidence and preparation.
| Risk Area | What Can Happen | Why It’s Serious | Your Protection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employment | Job loss, failed screening, suspension | Most workplaces have zero-tolerance drug policies | Disclose prescriptions before testing with documentation |
| Legal Issues | DUI charges, probation violations, custody disputes | Cannot drive or fulfill legal obligations while impaired | Carry prescription records; inform the attorney of all medications |
| Medical Care | Labeled drug-seeking, denied pain treatment | Providers may refuse future controlled substances | Be transparent about all medications upfront |
| Professional Licenses | Suspension, mandatory monitoring, discipline | Regulatory boards enforce strict substance standards | Report prescriptions when required; follow all policies |
| Insurance | Higher premiums, denied coverage claims | Insurers view positive tests as risk factors | Document legitimate medical necessity with providers |
A positive codeine test isn’t automatically problematic if you have legitimate documentation. The real trouble starts when you can’t verify your prescription or when you’ve been dishonest about medication use.
Resources & References
For authoritative information on codeine detection, metabolism, and safety, I recommend consulting these trusted medical and governmental sources.
The FDA provides comprehensive opioid prescribing guidelines at https://www.fda.gov, while the National Institutes of Health offers detailed pharmacological data at https://www.nih.gov.
SAMHSA maintains extensive resources on opioid treatment and drug testing protocols at https://www.samhsa.gov.
The Mayo Clinic provides patient-focused information on codeine metabolism and side effects at https://www.mayoclinic.org. Finally, the CDC offers evidence-based guidance on prescription opioid use and monitoring at https://www.cdc.gov.
These organizations regularly update their materials to reflect current clinical research and regulatory standards.
Summing It Up
Understanding codeine detection isn’t just about passing tests; it’s about making informed decisions regarding your health, career, and legal standing.
I’ve walked you through the science behind metabolism, shown you how different tests work, and explained why your individual biology matters so much.
Remember that detection windows are estimates, not guarantees, and factors like liver function and genetics create significant variation between individuals.
If you’re facing a drug test or managing codeine therapy, use this knowledge to plan appropriately and maintain proper documentation. Have questions or experiences to share? Drop a comment below; I’d love to hear your perspective.